A new CWCI study measures the level of attorney involvement in Calif WC indemnity claims, and provides regional data on average payments and claim closure rates for these claims.
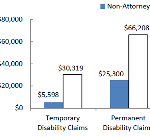

A new CWCI study measures the level of attorney involvement in Calif WC indemnity claims, and provides regional data on average payments and claim closure rates for these claims.
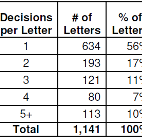
Medical dispute resolution is a vital component of all healthcare delivery systems. This study examines the key linkages between utilization review (UR) and independent medical review (IMR).
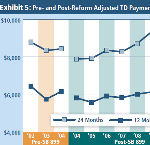
CWCI’s latest study tracks the Calif WC medical and indemnity benefit growth trends from AY 2002 – 2012
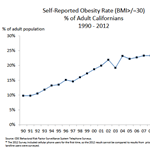
A new CWCI report examines the implications of the AMA’s recent reclassification of obesity as a treatable disease, and identifies and measures key differences between claims with and without obesity as a co-morbidity.
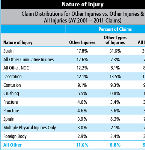
The latest CWCI Injury Score Card provides detailed data on claims in which the diagnosis falls in the “Other Injury, Poisoning and Toxic Effect category, which comprise 1 out of every 13 California workers’ comp claims, but 1 out of every 10 loss dollars.”
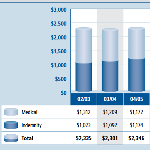
California Public Self-Insureds Reported Fewer Claims in 2012, But Claim Costs Remained Near 10-Year High
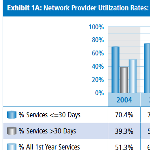
The latest research on network provider utilization in California workers’ compensation shows network physicians delivered nearly 80% of first-year, physician-based outpatient treatment on AY 2010 claims.
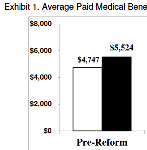
New CWCI Research shows California workers’ comp claims that involve physician-dispensed repackaged drugs have higher average medical and indemnity payments and more days away from work than comparable claims with no physician-dispensed repackaged drugs.
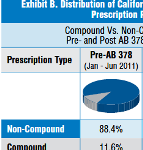
New CWCI research shows compound drugs accounted for a declining share of prescription medications dispensed to California injured workers last year, yet compound drug payments continued to represent a growing percentage of prescription dollars.
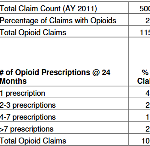
A new Institute analysis suggests that allowing workers’ comp payers access to data from the state’s prescription drug monitoring program (CURES) would help reduce inappropriate dispensing of opioids in workers’ comp, improving injured worker treatment and saving an estimated $57 million in AY 2011 claim costs.