CWCI research based on 10.8 million California workers’ comp prescriptions filled between 2005 and 2014 identifies trends in the volume, cost, potency and types of opioids used to treat injured workers over the past decade.
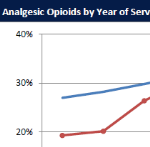

CWCI research based on 10.8 million California workers’ comp prescriptions filled between 2005 and 2014 identifies trends in the volume, cost, potency and types of opioids used to treat injured workers over the past decade.
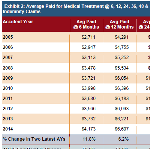
New CWCI research that tracks average California workers’ comp medical loss, indemnity benefit and medical cost containment (MCC) payments on AY 2005 – 2014 lost-time claims finds mixed results, with more developed data on older claims showing paid medical losses and indemnity leveling out or declining, and less developed data on newer claims indicating that average amounts paid in the early stages of a claim are on the rise.
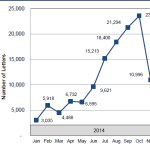
A detailed analysis on IMR outcomes, including decision counts and uphold rates, based on data gleaned from 2015 IMR determination letters
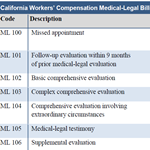
A CWCI study reviews statutory, regulatory and judicial changes to the California workers’ comp medical-legal process over the past quarter century, provides updated data on the quantity, mix and cost of medical-legal services following the 2002-04 reforms, and generates benchmark data for future research on the impact of the 2012 reforms, which introduced IMR as the new means for resolving treatment disputes.
New CWCI research based on 2014 UR data and IMR determinations from the first half of 2015 shows an estimated 96 percent of medical services in California workers’ comp are approved.
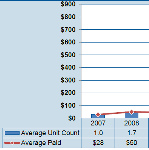
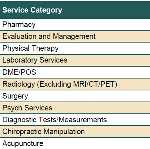
A new CWCI Report to the Industry examines the issue of Urine Drug Testing in California workers’ comp, which now accounts for nearly half of all lab services and more than half of all payments for lab services in the California system.
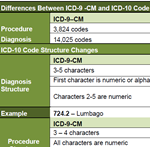
A new analysis examines the history, form and function of the ICD-10 classification system for healthcare delivery, which takes effect October 1 for all health care systems in the U.S. – including California workers’ comp.
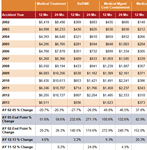
Initial data on AY 2014 lost-time claims indicate that average medical payments at 3 and 6 months post injury declined following implementation of SB 863, though the 12- and 24-month data on claims from prior years still show average losses trending up, led by ongoing increases in payments for prescription drugs and DME.
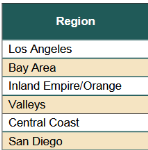
An analysis of 2015 independent medical review (IMR) decisions from the first quarter of 2015 shows no significant decline in IMR volume in the first three months of this year, even though the independent medical reviewers continue to concur with the utilization review (UR) physicians denial or modification of treatment in about 90 percent of the cases.
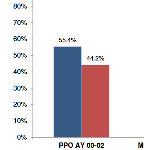
A new CWCI study examines changes in the use of physician networks in California workers’ comp from AY 2000 – June AY 2011, measures their impact on medical costs and compares the changing nature and characteristics of claims where treatment is managed inside and outside of networks.